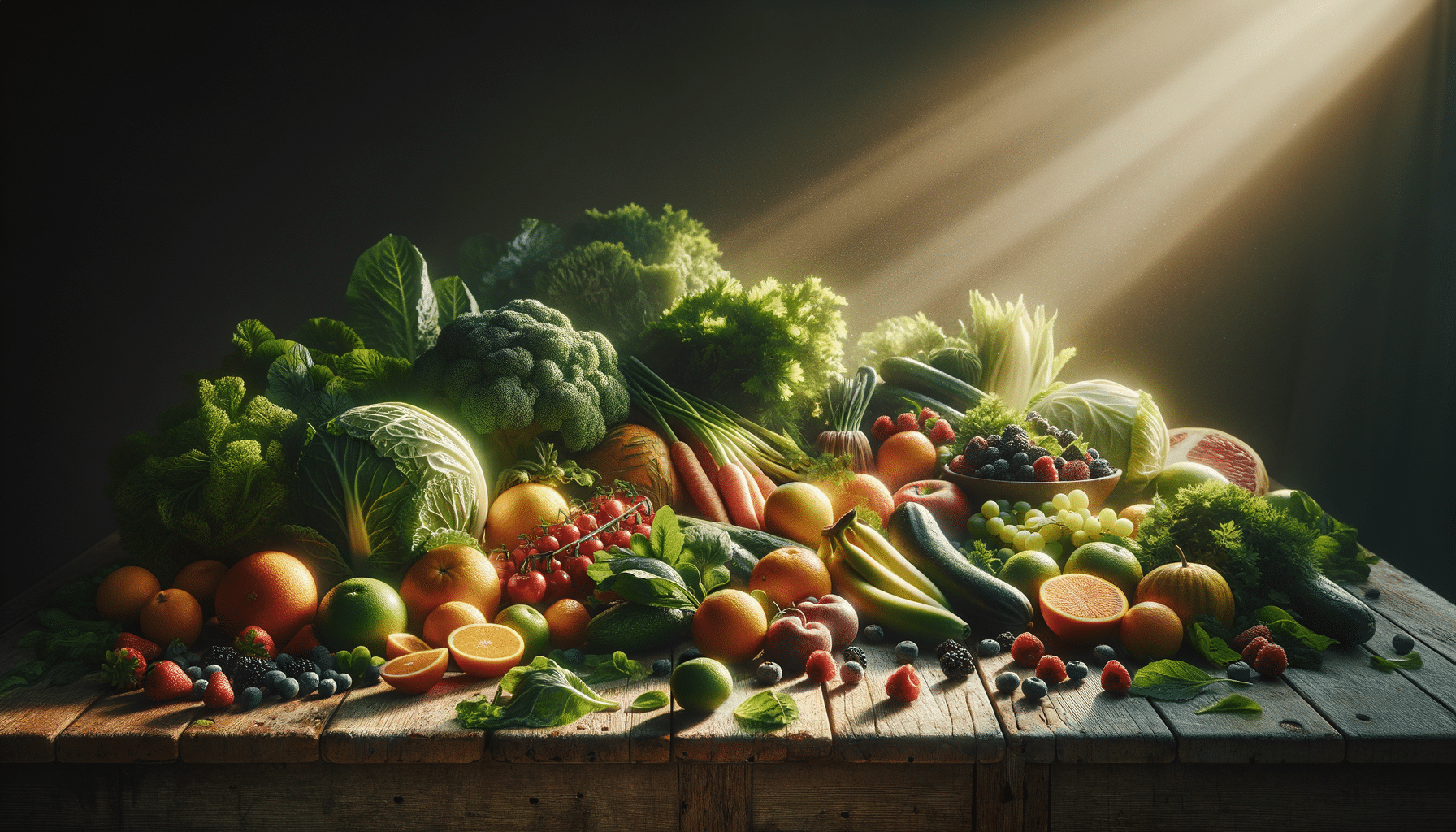
Dietary Considerations for Macular Degeneration
Introduction to Macular Degeneration and Diet
Macular degeneration is a common eye condition that affects the macula, the part of the eye responsible for central vision. This condition can lead to vision loss, particularly in older adults. While genetics and age are significant factors, lifestyle choices, including diet, play a crucial role in managing the progression of this condition. Understanding the relationship between diet and macular health is vital for those looking to maintain their vision.
A nutritious diet can contribute to eye health by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are implicated in macular degeneration. Research has shown that certain nutrients can help slow the progression of the disease. This article will explore various dietary considerations that may benefit individuals with macular degeneration.
Key Nutrients for Eye Health
The health of the eyes, particularly the macula, can be significantly influenced by specific nutrients. Antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, zinc, and beta-carotene have been studied for their potential to support eye health. These nutrients help combat oxidative stress that can damage the macula.
Moreover, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon and mackerel, have been associated with a reduced risk of macular degeneration. These fats are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial in managing the disease.
Incorporating leafy greens like spinach and kale into your diet can also be advantageous. These vegetables are rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that are concentrated in the macula and are known to filter harmful high-energy light waves.
The Role of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet that includes a variety of food groups can significantly impact eye health. Emphasizing whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting processed foods and sugars can help maintain overall health and potentially slow the progression of macular degeneration.
Fruits and vegetables should make up a large portion of daily intake. These foods are rich in essential vitamins and minerals that support eye health. Additionally, staying hydrated is crucial, as dehydration can exacerbate symptoms of eye strain and discomfort.
While a balanced diet is crucial, it is also essential to avoid certain foods that may negatively impact eye health. High-fat and high-sugar diets can increase the risk of developing macular degeneration and other health issues.
Supplements and Their Benefits
For some individuals, obtaining the necessary nutrients through diet alone may be challenging. In such cases, dietary supplements can be a beneficial addition to help fill nutritional gaps. Supplements containing antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and other eye-specific nutrients can support macular health.
However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any supplement regimen. They can provide guidance on appropriate dosages and ensure that supplements do not interact with other medications or conditions.
While supplements can provide benefits, they should not replace a healthy diet. They are most effective when used in conjunction with a balanced and nutrient-rich diet.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices
Understanding the impact of diet on macular degeneration is crucial for those looking to manage this condition effectively. By focusing on nutrient-rich foods and considering supplements when necessary, individuals can support their eye health and potentially slow the progression of macular degeneration.
Adopting a diet that includes a variety of vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide the necessary nutrients to maintain eye health. It is also important to consult with healthcare professionals to tailor dietary and supplement choices to individual needs.
Making informed dietary choices is a powerful step toward preserving vision and maintaining overall health.